Microwave Digital Circuits Made by way of Low-Value 3D Printer & Plastic Filament – 3DPrint.com
In the electronics industry, 3D printing has been used to make sensors, stretchable electronics, and compliant electronics, and to make waveguide devices and antennas for microwave devices. This is because this technology can be used to design dielectric substrates for certain applications and multilayer devices with multiple dielectric layers that will work with a variety of materials at different densities.
A team of researchers from the Miguel Hernández University of Elche in Spain has published a study entitled “Inexpensive Additive Manufacturing Techniques for Designing Microwave Planar Circuits Using Fused Deposition Modeling”. The paper describes her work with an inexpensive FDM 3D printer and plastic-based filaments to manufacture and implement microwave electronic circuits.
“Since all commercial filaments available for this type of 3D printer are not intended for the implementation of microwave devices, the electrical parameters of each material (dielectric constant and dissipation factor) must be determined. Since FDM does not allow the printing of metallic materials and the conductive filaments currently available do not have high conductivity, it is also necessary for microwave circuits to develop a technique for metallizing 3D printed parts using copper plates attached directly to the substrate, as is the case with conventional high-frequency substrates, ”the researchers wrote. “Due to the manufacturing process of the circuit, which on the one hand includes the manufacture of a substrate on the basis of a pseudo-thermofounded layer of plastic and on the other hand the use of epoxy adhesives to bond the copper plates, it must be checked whether the entire process leads to a reliable structure. “
Prusa i3 BQ Hephestos 3D printer used in this work. (Photo: BQ Hephestos)
For this study, the team selected a low-cost Prusa i3 Hephestos 3D printer that uses extrusion-based FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) technology. The Cura software was used to adjust the various 3D printing parameters below for all of the materials used.

The researchers analyzed many standard filaments with a diameter of 1.75 mm in order to “obtain different electrical properties for the design of microwave circuits” and selected these for the study:
- PLA from German RepRap: polymer made from lactic acid molecules
- ABS from Fillamentum: amorphous, impact-resistant thermoplastic
- Iglidur I180-PF (Tribo) by Igus: friction-resistant, good response to deterioration in wear
- ASS from Fillamentum: UV- and water-resistant thermoplastic
- PLA stainless steel from Protopasta: made of PLA and polished filament made of powdered stainless steel
- Laybrick filament from CC-PRODUCTS: made of sandstone, offers a surface texture similar to ceramic or stone
- Taulman nylon 230 filament: synthetic polyamide
- LayWoo-D3 filament from CC-PRODUCTS: Made from wood fibers and PLA, offers a similar surface texture to wood
- Smartfil EP filament by Fillamentum: Made from PLA and calcium carbonate, offers a surface texture similar to limestone
As you can see below, the sheets that make up the 3D printed microwave circuit substrates can be classified as either an outer layer or an inner layer. Because the mechanical stiffness of the substrate can be affected by the thickness of the outer layers, the team states that they should be “solid with a fill pattern density percentage of 100%” and made in a linear pattern to reduce surface roughness and avoid porosity . However, it doesn’t matter which fill density or which fill pattern is used for the inner layers.

(a) Structure of the printed layers of the substrates. (b) Linear printing pattern of 3D material with different filling densities, 100%, 50% and 15%.
The 3D printed substrate was metallized by attaching two 35 µm hydraulic pressed copper sheets to each side using a 2216 B / A non-conductive epoxy GRAY adhesive. The researchers built the microwave circuits using a Protomat S42 from the LPKF numerical control milling machine, and once the adhesive has solidified the copper on the substrate, it can be used.

(a) Manufacturing process for printed circuit boards. (b) Printed circuit structure of the various materials.
Manufacturing defects such as bubbles and voids between layers, lack of homogeneity in the layers, or too much adhesive can lead to possible failure of the structural integrity and performance of the 3D printed circuit. To “verify the correct metallization and fabrication of the substrate,” the team used fast and accurate, but inexpensive, ultrasonic non-destructive techniques to perform structural analysis, and turned to the time and frequency domain analysis techniques of circuit C-scans when there were any structural problems or there were defects.

(a) Setup for the measurements of the dielectric permittivity and the loss tangent. (b) Resonator and transmission line on different materials: ABS, PLA and ASA. (c) Electrical properties calculated for different substrates.
In addition, the researchers characterized the electrical properties of each filament in the microwave frequency range and implemented both standard and novel microwave filters in microstrip and stripline technology.

(a) Resonator and transmission line for PLA with densities of 70%, 50% and 15%. (b) Electrical properties for different filling densities of the PLA substrate.
Ultimately, the team designed and manufactured simple planar microwave circuits in a proof-of-concept to demonstrate how feasible it is to use 3D printing for this application.
“The designed devices were manufactured and measured with good results, demonstrating the possibility of using low-cost 3D printers in the design process of microwave planar circuits,” they write.

From left to right, from top to bottom: successive layers within the circuit in steps of approximately 150 µm.
By following this team’s methodology, other researchers could learn to add more complex microwave circuit structures to their work, including designing waveguide filters “using periodic structures where the additive techniques allow the waveguide sections to be designed to obtain higher rejection bandwidth”. and where the correct configuration of the 3D printer enables the design of a “coupling factor of the various filter sections”.

(a) Step impedance filter made with 100% density. (b) Measured and simulated response of the step impedance filter with a substrate with 100% density.
“The ultrasonic structure analysis has shown the reliability of the manufacturing process. In order to check the various possibilities of the additive manufacturing process presented, various simple and complex step impedance filters were finally implemented in microstrip and stripline technology. Both technologies have achieved good results, with better performance when additive options such as different substrate densities are used. Hence, it can be concluded that additive manufacturing techniques offer wide possibilities in the design of planar microwave circuits, ”the researchers concluded.

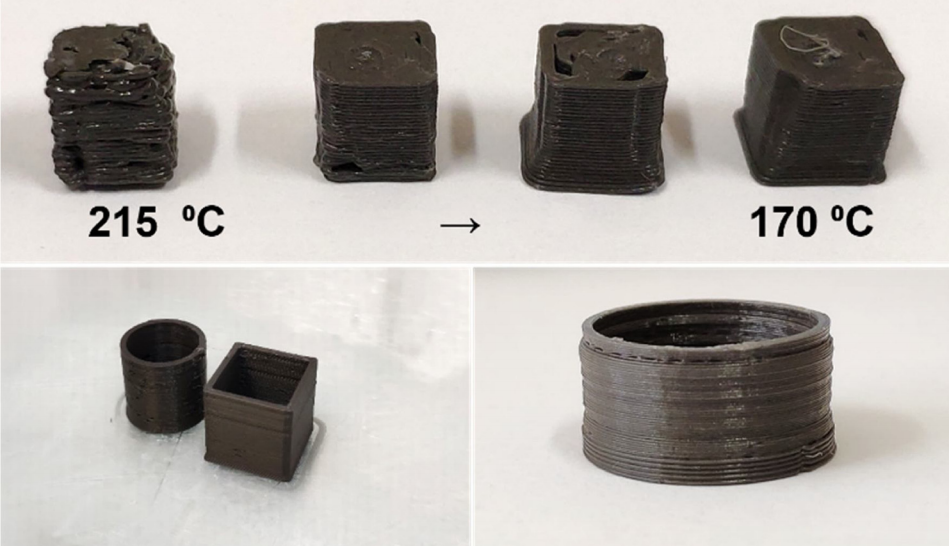
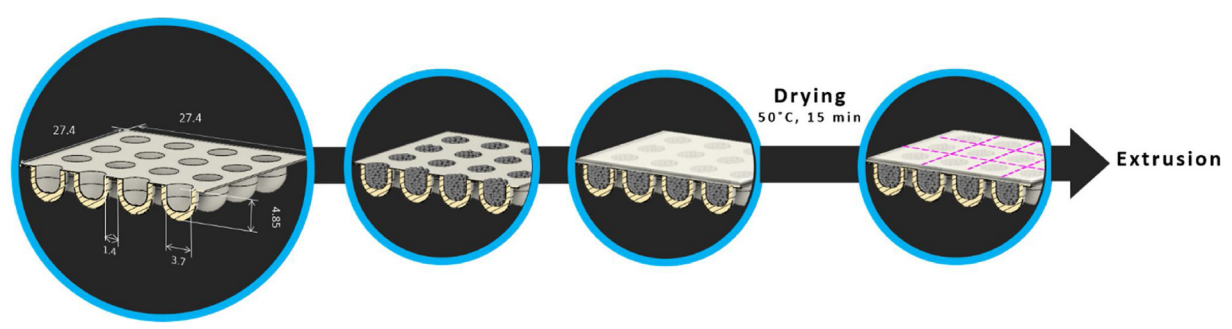 Printing and filling the capsules. Image via the University of Seville.
Printing and filling the capsules. Image via the University of Seville.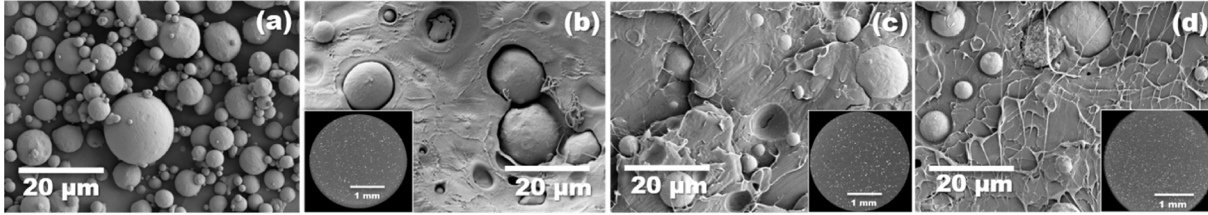 SEM image of the magnetic steel in the PLA matrix. Image via the University of Seville.
SEM image of the magnetic steel in the PLA matrix. Image via the University of Seville.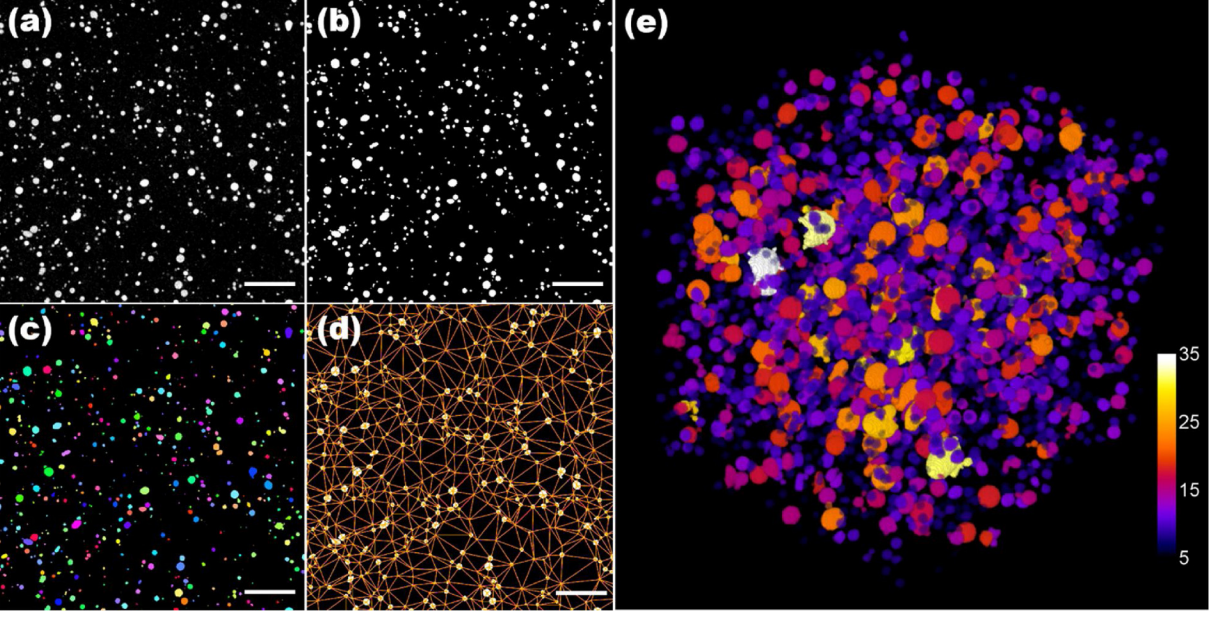 X-ray tomography showing the even distribution of the steel in the PLA matrix. Image via the University of Seville.
X-ray tomography showing the even distribution of the steel in the PLA matrix. Image via the University of Seville.