share
Tweet
share
share
...
Tag Archives: Printing
3D printing palms on: Some fascinating Jedi-level PLA filament secrets and techniques
20
Dec
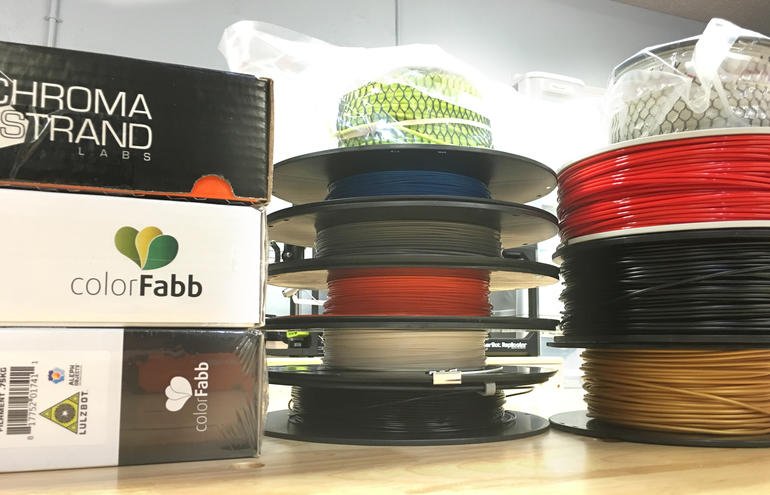
Eine Auswahl an Filamenten.Die meisten Desktop-3D-Drucker verwenden den sogenannten FDM...
RIZE debuts RIZIUM Glass Fiber filament for full-color 3D printing
20
Dec
3D printer manufacturer RIZE has presented its new long lasting RIZIUM fiberglass Filament for use with its 3D printers. The co...
HT vs PLA Filament for Excessive-Temperature 3D Printing
20
Dec
PLA or HT? Which high temperature filament can withstand heat and stress better?In my last article, I covered the basics of working w...
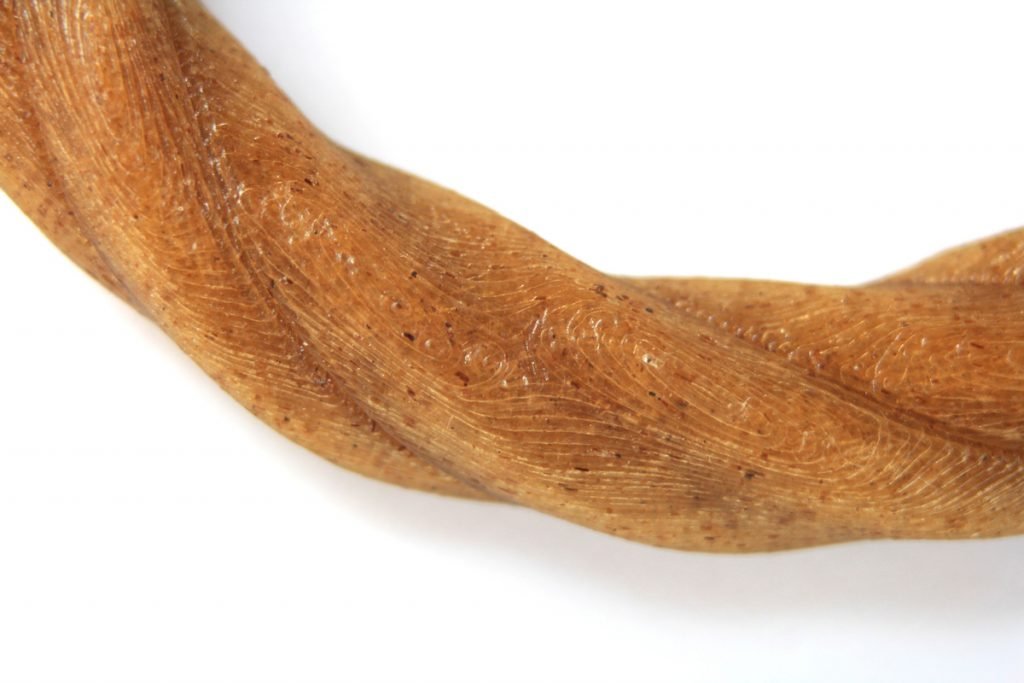
Hemp PLA Filament, Entwined, Launched by 3D Gas » 3D Printing Media Community
19
Dec
The wait - 3D printing with hemp filament! Entwined is a 3D printing filament made from industrial hemp grown and processed in the...
New & Improved PETG: Taulman3D Releases TECH-G 3D Printing Filament with Excessive Energy, Restricted Elongation – 3DPrint.com
19
Dec
The world of materials for 3D printing has grown huge, as has...
RIZE launches RIZIUM Glass Fiber composite filament » 3D Printing Media Community
19
Dec
The 3D printing company RIZE has expanded its material portfolio with the introduction of RIZIUM Glass Fiber (GF), a composite filamen...
Evonik develops the “world’s first” PEEK filament in implant-grade high quality for 3D printing
19
Dec
Evonik claims it is the first company in the world to have developed a polymer filament based on polyetheretherketone (PE...
World first: Implant-grade PEEK filament developed for 3D printing
18
Dec
The chemical company Evonik (Essen, Germany) has announced the develop...