Swedish 3D printing material developer Additive composite Uppsala and Add North 3D worked together to develop a polymer composite for radiation protection applications.
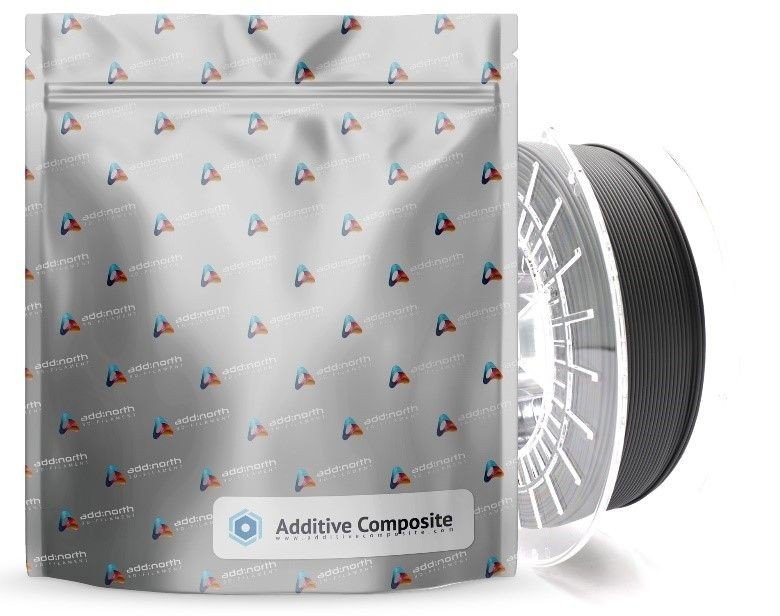
The material called Addbor N25 is a combination of boron carbide and nylon and was developed and manufactured as a filament optimized for 3D printing. The radiation protection capabilities are provided by the boron carbide element which provides effective absorption against neutrons. Additive Composite explains that the material can therefore be useful in research facilities, in the nuclear industry or in other places where radiation sources are used. Addbor N25 can be purchased from the Additive Composite website starting at SEK 9,500 ($ 988) / 750g.
Adam Engberg, CEO of Additive Composite stated, “Additive manufacturing is changing the number of products that are designed and manufactured. We believe that Addbor N25 is contributing to this development and helping both industry and large research institutions to replace toxic materials that could ultimately contaminate the environment. “
“Our new product is the first in a series of radiation protection materials that we are currently developing.”
The Addbor N25 filament. Photo via Additive Composite.
Filament production in Sweden
Additive Composite was founded in 2018 and aims to develop new solutions for research and commercial applications that take advantage of additive manufacturing. The company, based in Uppsala, a city near the Swedish capital Stockholm, mainly focuses on the development and marketing of composite materials for additive manufacturing.
With its developed materials, the company also offers an additive manufacturing service for users to manufacture individual custom components as well as small to medium-sized batches. The composite selection for Additive Composites includes gadolinium oxide (Gd2O3) composites, tungsten composites and more.
Add North 3D, on the other hand, is a filament manufacturer that mainly deals with the production of sustainable plastics such as PLA, which are made from renewable resources such as corn starch. Part of the company’s bioplastics research is funded by the Swedish government innovation agencies Vinnova and Almi.
Add North 3D not only develops novel materials with Additive Composite, but also maintains an established partnership with other Swedish developers of graphene nanocomposite materials Graphmatech. The two companies formed a partnership in 2018 to develop a new range of Graphene-based materials for use with FFF / FDM technology. This led to the development of Koltron G1, their first jointly developed product, made with Graphmatech’s Aros graph Material. The filament is a highly electrically and thermally conductive polymer for additive manufacturing. It is also flame retardant and resistant to a range of chemicals, UV light and high continuous working temperatures.
The Addbor N25 filament
The development of the Addbor N25 filament is based on original research at Uppsala University. The material, combined with the freedom of design offered by 3D printing, was designed to provide effective shielding against scattered radiation, as manufacturers can create complex shapes for any situation.
Additive Composite explains that the new filament is a suitable alternative to cadmium metal, a toxic metal commonly used in industrial workplaces. The company suggests that with the added benefit of geometric flexibility, the Addbor N25 filament could potentially replace the use of cadmium for radiation protection applications. Boron carbide makes up 25 percent of the total weight of the filament. The nozzle temperature of the Addbor N25 is between 250 and 270 degrees, has a tensile strength of 50 to 58 MPa and a flexural strength of 52 to 81 MPa.
Subscribe to the 3D printing industry newsletter for the latest news in additive manufacturing. You can also stay connected by following us Twitter and continue to like us Facebook.
Looking for a career in additive manufacturing? visit 3D print jobs for a selection of roles in the industry.
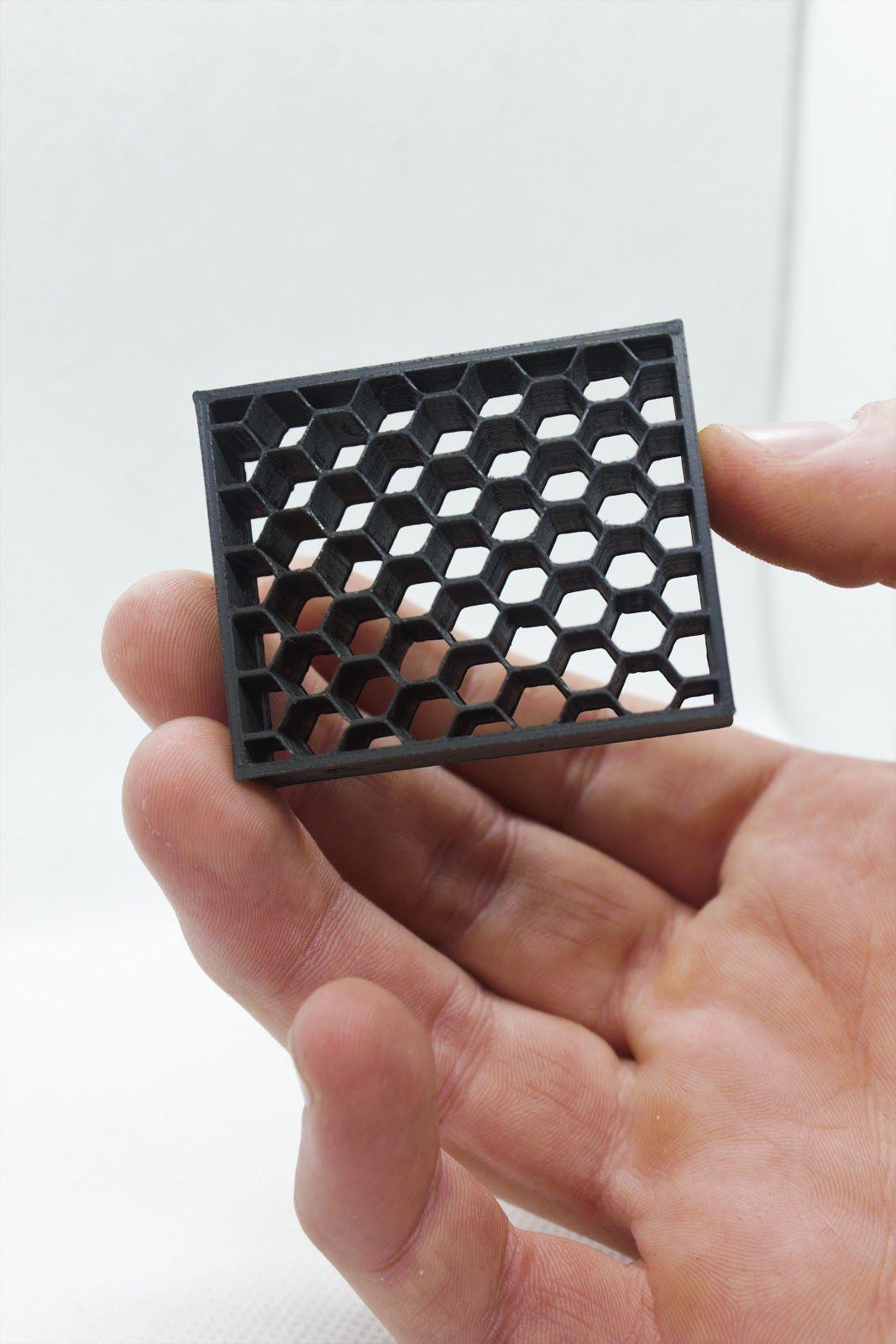
The picture shown shows a part 3D printed with the Addbor N25 filament. Photo via Additive Composite.